chapter2
##1.REGISTERS > There are 18 active registers:16 data registers and 2 processor status registers.r0~r15 are visible to programmer.However,r13,r14 and r15 has special function.
- r13 is used as the stack pointer(sp) and stores the head of the stack in current processor mode
- r14 is called the link register(lr) and is where the core puts the return address
- r15 is the program counter(pc)and contains the address of the next
- instruction to the be fetched by the processor.
There arm two program status register:cpsr and spsr(the current and saved program status registers,respectively)
which registers are visible the program depend on the current mode of the processor.
2.CURRENT PROGRAM STATUS REGISTER
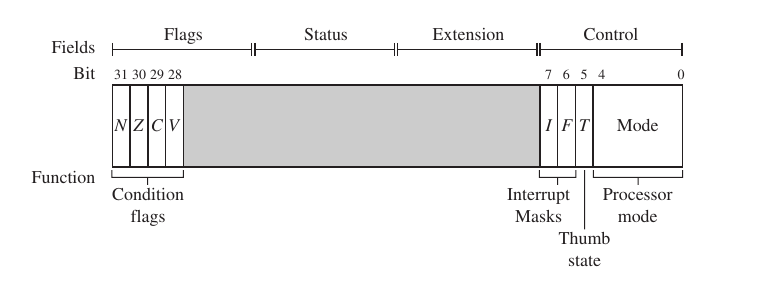 > the cpsr is divided into four fields:flags,status,extension,and contorl
the extension and status fields arm reserved for future use.the contorl fields
contains the processor mode,state,and interrupt mask bits.the flags fields contains the condition flags.
> the cpsr is divided into four fields:flags,status,extension,and contorl
the extension and status fields arm reserved for future use.the contorl fields
contains the processor mode,state,and interrupt mask bits.the flags fields contains the condition flags.
2.1 PROCESSOR MODES
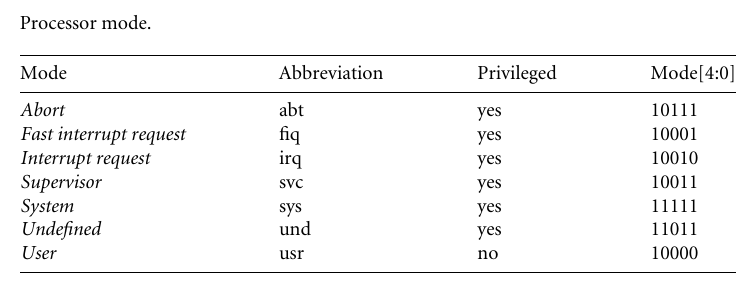
There are seven processor modes in total:six privileged modes(abort,fast interrupt request,interrupt request,supervisor,system,and undefined) and one onnprivileged mode(user)
- abort mode:there is a failed attempt ro access memory.
- Fast interrupt request and interrupt request mode:correspond to the two interrupt levels available on the arm processor.
- supervisor mode:the mode that the processor is in after reset and is genernally the mode that an operating system kernel operats in.
- system mode:special version of user mode that allows full read-write access to cpsr
- user mode:the mode is used for programs and application
2.2 BANKED REGISTER
the figure show below are all 37 registers.of those,20 registers are hidden from a program at differnt times.these registers are called banked registers.they are only available when the processor is in particular mode
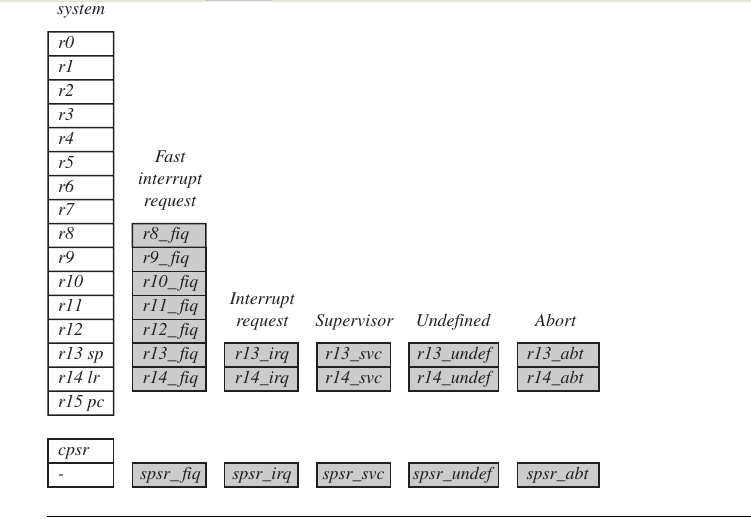
cpsr is not copied into the spsr when a mode change is forced due to a program writing directly to the cpsr.The cpsr only occurs when an exception or interrupt is raised.
2.3 INTERRUPT MASKS
interrupt masks are used to stop specific interrupt requests from interrupting the processor.
The cpsr two interrupt masks bits,7 and 6,orI and F,which control the masking of IRQ and FIQ.The I bit masks IRQ when set to binary 1,and similarly the F bit masks FIQ when set to binary 1.
2.4 CONDITION FLAGS
Condition flags are updated by comparisons and the result of ALU operations that specify the S instruction suffix.

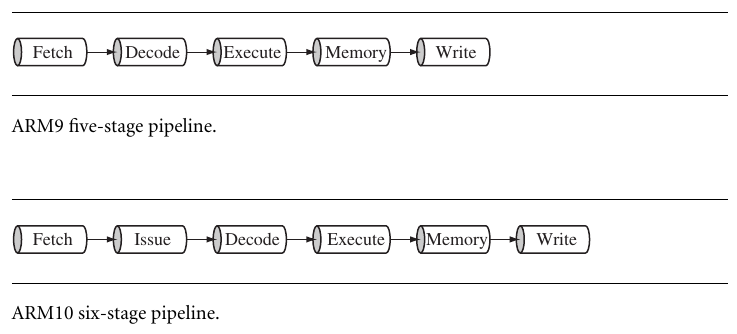
2.PIPLINE
A pipeline is the mechanism a RISC processor uses to execute instructions.
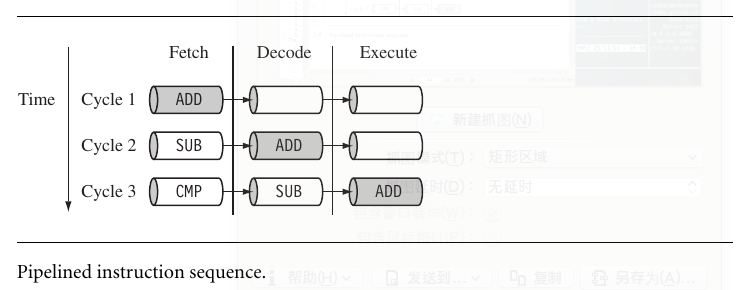
the stage of arm pipeline:
3.EXCEPTIONS,INTERRUPTS,AND THE VECTOR TABLE
The memory map address 0x00000000 is reserveda for the vector table,a set of 32-bit words.On some processor the vector table can be optionally located at a higher address in memory(starting at the offset 0xffff0000).such as linux and microsoft’s embeded products an take advantage of this feature.
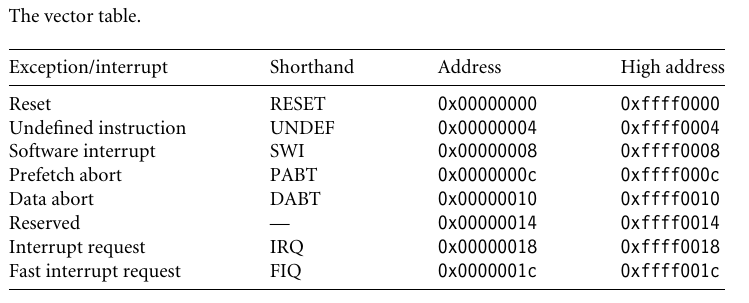
- Reset vector is the location of the first instruction executed by the processor when power is applied.this instruction branches to initialization code.
- Undefined instruction vector is used when the processor cannot decode an instruction.
- Software interrupt vector is called when you execute a SWI instruction.The SWI instruction is frequently used as the mechanism to invoke an operating system routine.
- Prefetch abort vector occurs when the processor attempts to fetch an instruction from an address without the correct access permissions.The actual abort occurs in the decode stage.
- Data abort vector is similar to prefetch abort but is raised when an instruction attempts to access data memory without the correct access permissions.
- Interrupt request vector is used by external hardware to interrupt the normal execution flow of the processor.It can only be raised if IRQs are not masked in the cpsr.
- Fast interrupt request vector is similar to the interrupt request but is reserved for hardware requiring faster response times.It can only be raised if FIQs are not masked in the cpsr.
4.CORE EXTENSION
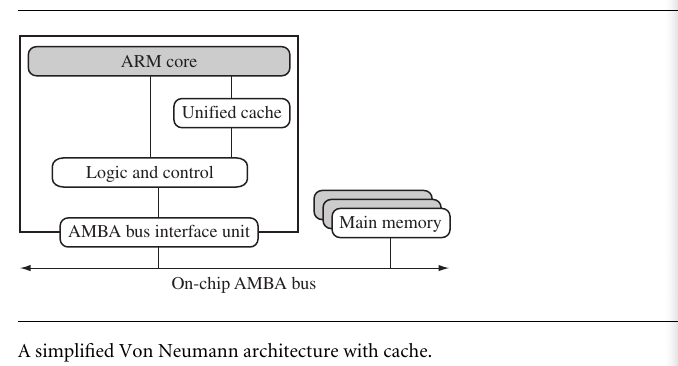
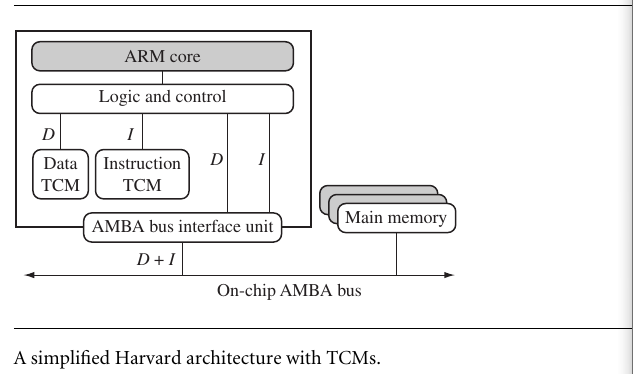
4.1 CACHE AND TIGHTLY COUPLED MEMORY
The cache is a block of fast memory placed between main memory and the core.It allows for more efficient fetched from some memory types.
There are two types cache of arm: - Von Neumann-style core - Harvard-style core
4.2 MEMORY MANAGEMENT
ARM cores have three differnt types of memory management hardware:
- Nonprotected memory is fixed and provides very little flexibility.It is normally used for small.simple embeded systems that requrie no protection from rogue applications.
- MPUs employ a simple system that uses a limited number of memory regions.These regions are controlled with a set of special corocessor registers,and each region is defined with specific access permissions.This type of memory management is used for systems that require memory protection but don’t have a complex memory map.The MPU is explained in chapter13.
- MMUs are the most comprehensive memory management hardware available on the ARM.The MMU uses a set of translation tables to privide fine graimed control over memory.These tables are stored in main memory and provides a virtual-to-physical address map as well as access permissions.MMUs are designed for more sophisticated platform operating system that support mutitasking.The MMU is explained in chapter14.
4.2 COPROCESSORS
Coprocessors can be attached to the ARM processor.A coprocessor extends the processing feature of a core by extending the instruction set or by providing configuration registers.More than one coprocessor can be added to the ARM core via the coprocessor interface.